Microsoft is fundamentally changing Windows 11, transforming it from a traditional operating system into what it calls an “agentic OS” – one driven by artificial intelligence. The core of this shift is integrating AI agents directly into the Windows taskbar, enabling them to autonomously perform tasks on your behalf. This isn’t just about adding AI features; it’s about making AI an active, behind-the-scenes assistant within the OS itself.
The Rise of AI Agents in Windows
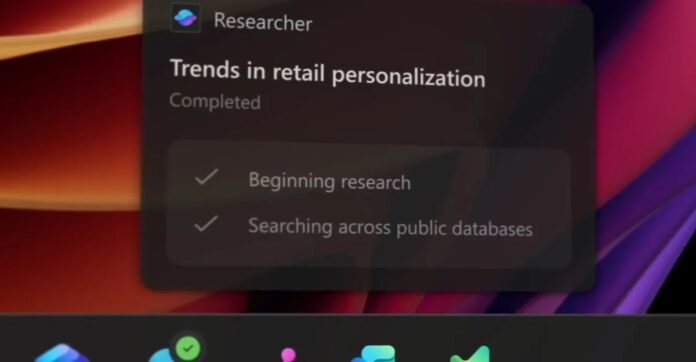
The company is embedding AI agents, including its own Microsoft 365 Copilot and third-party options, directly into the Windows 11 taskbar. These agents can work independently, researching data, automating tasks, or even accessing files while you continue working on other things. Microsoft emphasizes that users will always know what an agent is doing, with real-time status updates and notifications via taskbar badges.
This shift is significant because it moves beyond passive AI tools to an operating system that actively acts on your behalf. The new Ask Copilot feature blends file search with AI capabilities, allowing users to launch AI agents directly from the taskbar.
How Agents Function: Security and Control
Microsoft is taking security seriously. AI agents operate in a secure, isolated “workspace” – a sandbox environment with its own Windows account – to prevent errors from affecting your primary system. This is partly due to the potential for inaccurate AI responses, so keeping agent activity separate offers an added layer of protection.
Users retain control; the AI features are opt-in only. Microsoft stresses that customers can decide when and how they engage with Copilot and its agents.
The Tech Behind Agentic OS: MCP and Beyond
The foundation for this transformation is the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This standardized framework allows AI agents to discover and interact with tools and other agents securely on your device. It also enables Microsoft to provide an “agentic framework” for these tools.
Microsoft is also integrating Copilot directly into File Explorer, enabling instant summaries, answers, and even email drafts based on document content. The “Click to Do” feature on Copilot Plus PCs lets you convert data from tables into Excel spreadsheets.
Hybrid AI: Local and Cloud Power
Microsoft is blending local AI processing (on Copilot Plus PCs) with cloud-powered AI capabilities. Features like offline writing assistance on Copilot Plus PCs demonstrate this hybrid approach. Other AI features, such as AI-generated summaries in Outlook and automatic alt-text in Word, are also rolling out.
The company is even expanding AI to its cloud-based Windows 365 service, providing Copilot Plus features and full cloud access.
Security and IT Focus
Alongside AI advancements, Microsoft is also enhancing Windows security. Hardware-accelerated BitLocker will be integrated into future Windows devices, requiring new chips. Sysmon functionality is coming in 2026, improving security event management. A visual refresh of Windows Hello and passkey manager integration with popular tools like 1Password and Bitwarden are also planned.
Ultimately, Microsoft’s goal is to make Windows an operating system that anticipates your needs and automates tasks, fundamentally altering how users interact with their PCs. This is a long-term strategy that will redefine what an OS can do, shifting from a passive tool to an active, intelligent assistant.